Renewable Energy Basics: A Guide to Sustainable Power Solutions
In today’s world, where environmental concerns are at the forefront of global discussions, renewable energy has emerged as a crucial solution for sustainable power generation. Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower provide alternatives to traditional fossil fuels, which are increasingly contributing to climate change. This article will take you through the basics of renewable energy, its types, benefits, and how it is revolutionizing the energy sector.

What is Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy refers to power derived from resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. These resources include sunlight, wind, rain, tides, geothermal heat, and more. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and contribute to environmental degradation, renewable energy sources are sustainable and have minimal impact on the environment.
Key renewable energy sources include:
-
Solar Power: Capturing sunlight and converting it into electricity.
-
Wind Power: Using wind turbines to generate electricity.
-
Hydropower: Harnessing water flow to produce energy.
-
Geothermal Energy: Tapping into the heat stored beneath the Earth’s surface.
-
Biomass Energy: Using organic materials to generate power.
Why is Renewable Energy Important?
As the world faces the challenges of climate change and diminishing natural resources, renewable energy offers a path toward a cleaner, greener future. Here are some key reasons why renewable energy is so important:
1. Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Traditional energy sources, like coal and natural gas, release greenhouse gases (GHGs) into the atmosphere, which contribute to global warming. Renewable energy systems produce little to no GHGs, making them a much cleaner alternative.
2. Sustainability
Unlike fossil fuels, which take millions of years to form, renewable resources are naturally replenished in a short amount of time. Solar energy, for example, will be available as long as the sun shines.
3. Energy Security
Investing in renewable energy sources reduces reliance on imported fossil fuels, providing greater energy security. This is especially important for countries seeking to stabilize their energy supply.

Types of Renewable Energy Sources
1. Solar Energy
Solar energy is the most widely used renewable resource. By using photovoltaic cells (solar panels), sunlight is converted into electricity. There are two primary ways to harness solar energy:
-
Photovoltaic (PV) Systems: These panels convert sunlight directly into electricity.
-
Solar Thermal Systems: These systems use sunlight to heat water or air for heating purposes.
Benefits of Solar Energy:
-
It can be used in homes, businesses, and large-scale power plants.
-
Solar panels have low maintenance costs and long lifespans.
2. Wind Energy
Wind energy is harnessed by wind turbines that capture the movement of air to generate electricity. This form of energy is incredibly efficient and is especially useful in areas with consistent wind patterns.
Benefits of Wind Energy:
-
Wind turbines produce large amounts of electricity with no emissions.
-
Wind energy is highly scalable, from small residential turbines to large offshore wind farms.
3. Hydropower
Hydropower uses water flow to produce energy, typically through dams. As water flows over the dam, it spins turbines, which then generate electricity. This is one of the oldest and most widely used renewable energy sources.
Benefits of Hydropower:
-
Hydropower provides a reliable, steady source of electricity.
-
It can be used for large-scale energy production.
4. Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy taps into the heat from beneath the Earth’s surface. By accessing hot water or steam reservoirs, this energy can be used to generate electricity or for direct heating applications.
Benefits of Geothermal Energy:
-
Geothermal systems produce continuous, baseload energy.
-
It has a minimal carbon footprint and is highly sustainable.
5. Biomass Energy
Biomass energy is produced from organic materials such as wood, agricultural residues, and even algae. These materials are burned or converted into biofuels, which can be used for electricity generation, heating, or transportation.
Benefits of Biomass Energy:
-
Biomass helps reduce waste by converting organic materials into usable energy.
-
It can be a reliable source of energy in rural areas.
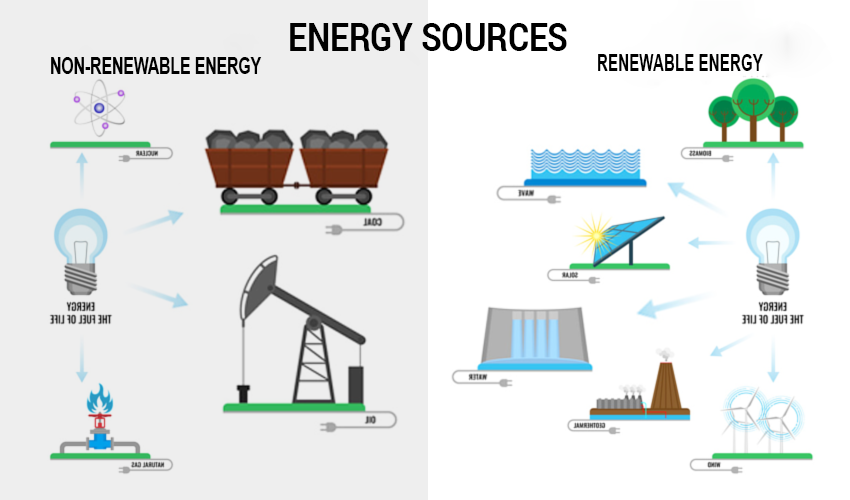
How Does Renewable Energy Work?
Renewable energy technologies convert natural resources into usable power. Here is a simple breakdown of how each type of renewable energy works:
-
Solar Power: Photovoltaic cells capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. In concentrated solar power (CSP) systems, mirrors or lenses focus sunlight to heat fluids, which then generate steam to drive turbines.
-
Wind Power: Wind turbines have large blades that spin when the wind blows. This movement generates electricity through a connected generator.
-
Hydropower: Water stored behind a dam flows through turbines, turning them to generate electricity.
-
Geothermal Energy: Wells are drilled into the Earth to access hot steam or water. This steam is used to turn turbines, which generate power.
-
Biomass: Organic materials are burned or converted into gases or liquids that can be used as fuel for electricity production or heating.
Benefits of Renewable Energy
1. Environmental Impact
The most significant benefit of renewable energy is its environmental impact. These energy sources produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions, reducing the overall carbon footprint of energy generation. This helps to mitigate climate change and decrease air pollution.
2. Job Creation
The renewable energy sector is a significant job creator. From manufacturing solar panels and wind turbines to installing and maintaining systems, the renewable energy industry provides millions of jobs worldwide.
3. Lower Operating Costs
Although the initial installation of renewable energy systems can be costly, they typically have lower operational and maintenance costs compared to traditional fossil fuel-based power plants. Over time, renewable energy systems pay for themselves through savings on energy bills.
4. Decentralization of Power Supply
Renewable energy sources can be deployed locally, reducing the need for large, centralized power plants. This decentralization can increase energy access in remote or underserved areas.
Challenges of Renewable Energy
While renewable energy offers numerous benefits, there are still challenges to overcome:
1. Intermittency
Some renewable energy sources, like solar and wind, are intermittent. This means they only produce electricity when the sun shines or the wind blows. However, advancements in energy storage technology, such as batteries, are helping to address this issue.
2. High Initial Costs
The upfront cost of renewable energy systems can be higher than traditional fossil fuel-based power generation. However, as technology advances and economies of scale are realized, costs are expected to continue to decrease.
3. Land and Space Requirements
Large-scale renewable energy installations, such as wind farms and solar power plants, require significant land area. This can lead to land use conflicts, particularly in densely populated regions.
The Future of Renewable Energy
The future of renewable energy is promising. Technological advancements are driving down costs and improving efficiency. With growing concerns over climate change and sustainability, governments and businesses worldwide are investing more in clean energy solutions.
In the coming years, we can expect to see:
-
Increased adoption of solar and wind energy, particularly in residential and commercial applications.
-
Improved energy storage technologies to combat intermittency issues.
-
Greater integration of renewable energy into existing power grids to ensure a stable energy supply.
FAQs About Renewable Energy
What are the main types of renewable energy?
The main types of renewable energy include solar power, wind power, hydropower, geothermal energy, and biomass energy.
How does solar energy work?
Solar energy works by capturing sunlight using photovoltaic cells, which convert it into electricity. Alternatively, concentrated solar power systems use mirrors to focus sunlight and produce heat for generating electricity.
Is renewable energy really affordable?
While the initial installation costs of renewable energy systems can be high, their operational costs are lower compared to fossil fuel-based systems. Over time, renewable energy can save money on energy bills.
What are the challenges of renewable energy?
Some challenges include intermittency (e.g., solar and wind energy depend on weather conditions), high initial costs, and the need for large spaces for installations.
Conclusion
Renewable energy is the key to a sustainable future. As technology improves and governments and businesses continue to invest in clean energy solutions, renewable energy will become the dominant source of power. By understanding the basics of renewable energy and supporting its adoption, we can all contribute to a cleaner, greener planet.
For more information on renewable energy solutions and how you can get involved, visit our Renewable Energy Resources page.
This guide provides an overview of renewable energy basics, its benefits, and challenges. It’s an exciting time for the energy sector, and understanding renewable energy is the first step toward embracing a sustainable future.