Global Citizenship Education: Preparing Students for a Connected World
Introduction: The Importance of Global Citizenship Education
As the world becomes more interconnected, the need for Global Citizenship Education (GCE) is more urgent than ever. It prepares students to navigate the complexities of a globalized world, helping them understand their role as responsible global citizens. GCE encourages awareness of global issues, empathy for others, and a sense of responsibility toward sustainable development.
Global Citizenship Education is not just about learning facts; it’s about fostering the skills, values, and attitudes that allow individuals to engage with the world thoughtfully. Whether it’s addressing climate change, promoting social justice, or encouraging cultural understanding, GCE plays a critical role in shaping the future of societies around the world.
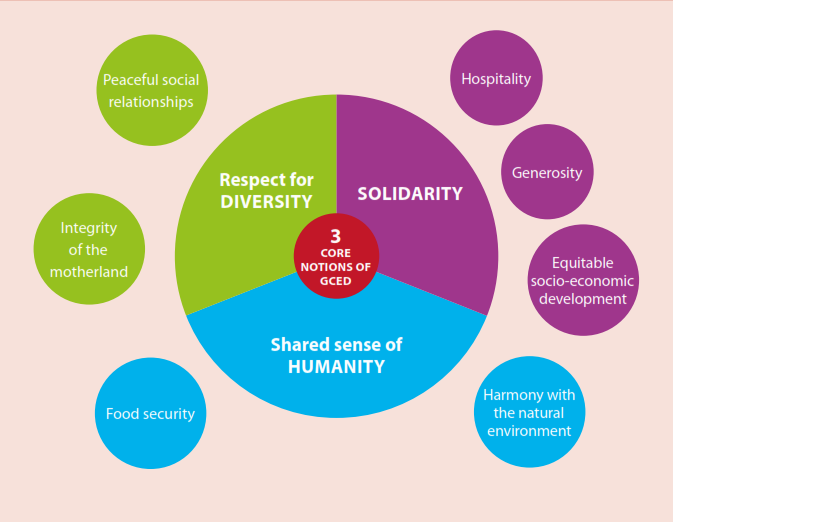
1. What is Global Citizenship Education?
Global Citizenship Education (GCE) is an educational framework designed to equip individuals with the knowledge, skills, and values needed to act as responsible global citizens. It focuses on promoting a sense of belonging to the global community, regardless of nationality, ethnicity, or culture. GCE fosters a deep understanding of global challenges and encourages proactive engagement in solving them.
GCE emphasizes critical thinking, active participation, and respect for diversity. It involves:
-
Awareness of global issues: Understanding the complex and interconnected challenges faced by humanity.
-
Empathy for others: Recognizing and respecting cultural differences while appreciating shared human values.
-
Action for change: Empowering individuals to take concrete steps toward positive change in their communities and the world.
By fostering these qualities, Global Citizenship Education helps individuals become informed, responsible, and engaged global citizens.
2. The Core Concepts of Global Citizenship Education
2.1 Understanding Interconnectedness
One of the key concepts in GCE is the recognition that global challenges are interconnected. Issues such as poverty, climate change, human rights, and conflict are not isolated problems but are deeply linked across borders. Understanding these connections is crucial for students to become active participants in global solutions.
Students are encouraged to think beyond national or regional perspectives and consider the global impact of local actions. This holistic approach to problem-solving fosters a mindset of collaboration rather than competition.
2.2 Promoting Social Justice and Equity
Global Citizenship Education focuses heavily on the principles of social justice and equity. It teaches students to understand the unequal distribution of resources, opportunities, and power in the world. This awareness leads to a sense of responsibility to address disparities and advocate for inclusive development.
Key topics within this area include:
-
Human rights: Understanding and respecting the rights of all individuals, regardless of their background or status.
-
Sustainability: Learning to balance economic development with environmental protection and social equity.
-
Gender equality: Promoting the importance of equal rights and opportunities for all genders.
2.3 Cultural Awareness and Respect
GCE also emphasizes the importance of cultural awareness and respect. In a world of diverse cultures and languages, it is crucial for students to learn how to interact with individuals from different backgrounds in a respectful and open-minded manner. This component helps reduce prejudice, stereotypes, and discrimination, while promoting harmony in diverse societies.
Students gain a deeper understanding of:
-
Cultural diversity: Recognizing and celebrating cultural differences rather than seeing them as barriers.
-
Global citizenship: Identifying as part of a global community, rather than focusing solely on national or local identity.
-
Empathy and inclusion: Building a foundation of empathy that encourages cooperation and respect in multicultural environments.
3. Why is Global Citizenship Education Important?
In an increasingly interconnected world, Global Citizenship Education is vital for several reasons:
3.1 Promoting Sustainable Development
Sustainability is one of the biggest challenges of our time. GCE equips students with the knowledge and skills to think critically about sustainable development. By understanding the complexities of climate change, resource depletion, and environmental degradation, students can contribute to creating sustainable solutions for the future.
3.2 Encouraging Global Peace and Security
Another key aspect of GCE is its role in promoting global peace and security. Education about conflicts, diplomacy, and human rights helps students understand the importance of peaceful resolution of disputes. GCE fosters a commitment to peace by promoting values of tolerance, respect, and dialogue over violence and war.
3.3 Preparing Students for a Global Workforce
As businesses and organizations increasingly operate on a global scale, cultural competence and international collaboration are essential skills in the modern workforce. GCE prepares students for this by teaching them how to work effectively with people from diverse cultural and national backgrounds. This makes them more competitive in the job market and more capable of contributing to global business solutions.
4. How to Implement Global Citizenship Education
4.1 Integrating Global Issues into the Curriculum
To ensure that students develop the skills necessary for global citizenship, global issues should be integrated into the curriculum at all levels of education. This can be done through:
-
Global studies programs: Offering courses that focus on international relations, global conflicts, and environmental sustainability.
-
Project-based learning: Encouraging students to work on projects that address real-world global challenges, such as climate change or poverty.
-
Collaborative learning: Partnering with schools from other countries to encourage cultural exchange and shared learning experiences.
4.2 Creating a Global Classroom Environment
Teachers can create a global classroom environment by incorporating diverse perspectives into their teaching. This can be achieved by:
-
Using multicultural teaching materials that represent a variety of cultures and viewpoints.
-
Inviting guest speakers from different backgrounds to share their experiences.
-
Encouraging open discussions about global issues such as human rights, climate change, and international conflicts.
4.3 Empowering Students to Take Action
It’s important to move beyond theoretical knowledge and empower students to take action. Service-learning programs, internships with international organizations, and involvement in community projects can give students the opportunity to apply what they’ve learned and make a real difference in their communities and the world.
5. The Benefits of Global Citizenship Education
5.1 Personal Development and Empowerment
One of the most significant benefits of GCE is that it fosters personal growth. Students who engage in global citizenship education develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills. These skills are essential for navigating a complex world and for making informed decisions that affect both local and global communities.
5.2 Fostering Tolerance and Understanding
GCE plays a crucial role in fostering tolerance and understanding across cultures. By teaching students about the challenges faced by people in different parts of the world, it encourages empathy and dismantles prejudices. This leads to a more harmonious society, where diversity is celebrated rather than feared.
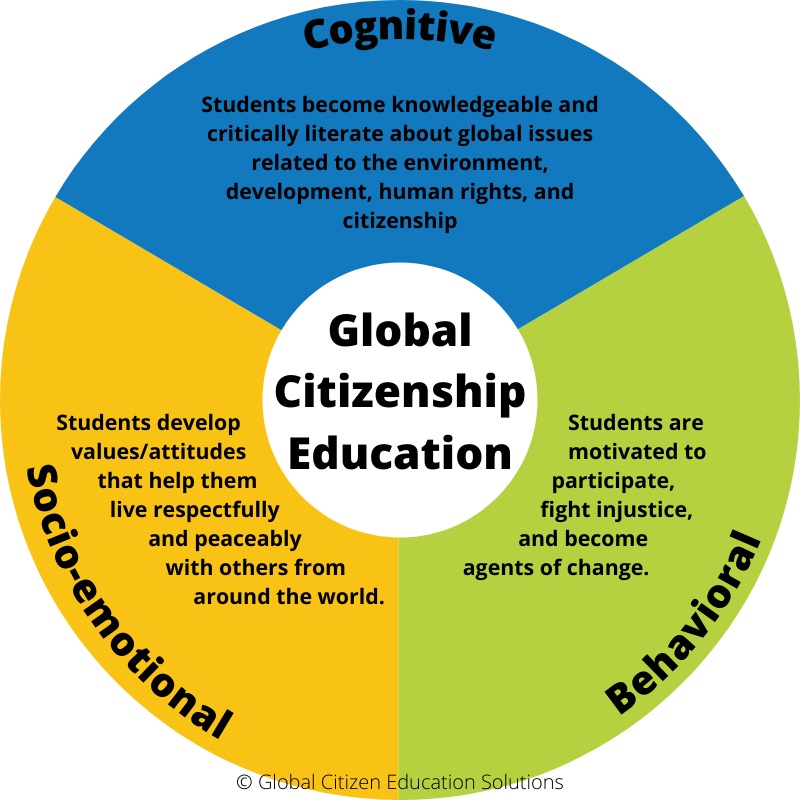
5.3 Building Stronger Communities
When students are taught the principles of global citizenship, they are more likely to become active and engaged citizens. They understand the importance of contributing to their local communities and working collaboratively to address local issues. GCE empowers individuals to build stronger, more resilient communities that are capable of addressing both local and global challenges.
6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the goal of Global Citizenship Education?
A1: The goal of Global Citizenship Education is to empower individuals with the knowledge, skills, and values necessary to understand and engage with global issues, promote social justice, and act as responsible members of a global community.
Q2: How can Global Citizenship Education be implemented in schools?
A2: GCE can be implemented by integrating global issues into the curriculum, fostering a multicultural classroom environment, and empowering students to take part in global projects and service-learning activities.
Q3: Why is Global Citizenship Education important for students?
A3: GCE helps students develop critical thinking skills, promotes empathy, and prepares them for the global workforce. It also encourages social responsibility, sustainability, and peaceful resolution of conflicts.
Q4: How does GCE contribute to sustainability?
A4: GCE educates students about environmental issues, human rights, and the importance of sustainable development. By raising awareness about these topics, students are empowered to take action toward a more sustainable future.
Conclusion: Shaping Future Global Citizens
Global Citizenship Education is crucial for preparing students to become active, responsible, and compassionate global citizens. By integrating global issues into the curriculum, promoting cultural understanding, and encouraging action, we can create a generation of individuals who are committed to addressing the world’s most pressing challenges. Through GCE, students learn to navigate a complex world with empathy, critical thinking, and a sense of responsibility, shaping a brighter and more sustainable future for all.










